Quarz
Material
Einkristalliner Quarz (SiO2) ist ein Kristall, der sowohl natürlich vorkommt als auch mittels Hydrothermalsynthese synthetisch hergestellt wird. Im Wellenlängenbereich zwischen 0,3 µm und 2,7 µm liegt der Transmissionsanteil über 90 %. Im Unterschied zu Quarzglas besitzt einkristalliner Quarz eine starke Doppelbrechung. Quarz liegt standardmäßig als alpha-Quarz (Tiefquarz) vor, bei einer Temperatur oberhalb von 573 °C ändert sich die Kristallstruktur in beta-Quarz (Hochquarz). Dabei handelt es sich um einen reversiblen Vorgang, der jedoch zu Rissen und Brüchen im Material führen kann.
Quarz wird hauptsächlich als Polarisator, in piezoelektrischen Bauelementen, in FIR-Optiken, als VUV-Filter sowie in Mikroskopen genutzt.
Eigenschaften
Spektrale Eigenschaften
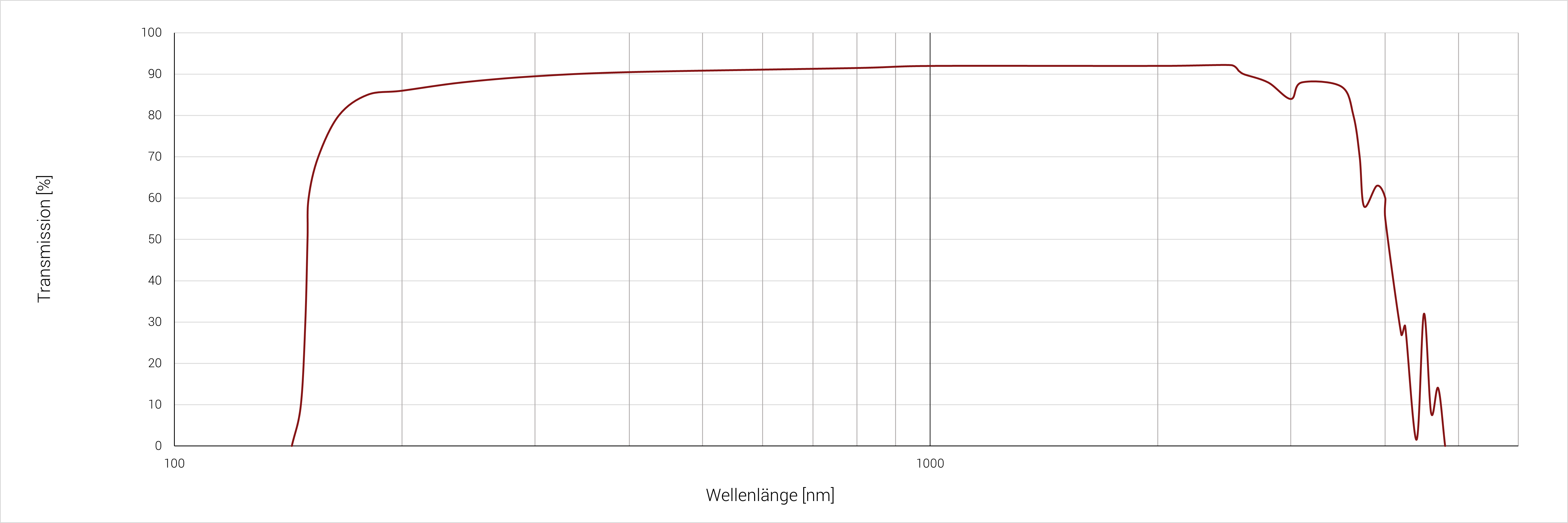
Probendicke: 2 mm
